INFLATION- RECESSION – DEPRECIATION
This course is for those students who want to know about management, investment, budgeting, advertising, and different cards.
Every country’s and family’s development is built on economics. Economics is a required course for all educated people; without it, you cannot claim to be educated.
Learn economics to better understand the ups and downs of the economy and how to manage your life. Economics enables you to think strategically and make decisions that optimize the outcome.
People who have studied Economics and Finance are in high demand because they are well-prepared for jobs in banking and the financial sector, such as in accounting firms.
The study of economics helps people understand the world around them. It enables people to understand people, businesses, markets, and governments, and therefore better respond to the threats and opportunities that emerge when things change.
INFLATION-DEPRECIATION-RECESSION
DEPRECIATION

- Straight Line Method.
- Written Down Value Method.
- Units of production method.
- Straight Line. This is the most common and simplest depreciation method.
- Declining Balance.
- Double Declining Balance. : Double declining balance depreciation is an accelerated depreciation method. Businesses use accelerated methods when dealing with assets that are more productive in their early years. The double declining balance method is often used for equipment when the units of production method is not used.
- Sum of the Years’ Digits. :Sum of the years’ digits depreciation is also an accelerated depreciation method. It doesn’t depreciate an asset quite as quickly as double declining balance depreciation, but it does it quicker than straight-line depreciation.
- Units of Production. Units of production depreciation is based on how many items a piece of equipment can produce. ..
To calculate depreciation using the straight-line method, subtract the asset’s salvage value (what you expect it to be worth at the end of its useful life) from its cost. The result is the depreciable basis or the amount that can be depreciated. Divide this amount by the number of years in the asset’s useful lifespan.
Depreciation examples: Let’s say you purchase a piece of equipment for $260,000. You anticipate using the equipment for eight years, and you anticipate the scrap value will be $20,000. The annual and monthly depreciation expenses for the vehicle using the straight-line depreciation method would be:
-
($260,000 – $20,000) / 8 = $30,000
-
$30,000 / 12 months = $2,500 per month
Find out what your annual and monthly depreciation expenses should be using the simplest straight-line method, as well as the three other methods, in the calculator below.
INFLATION
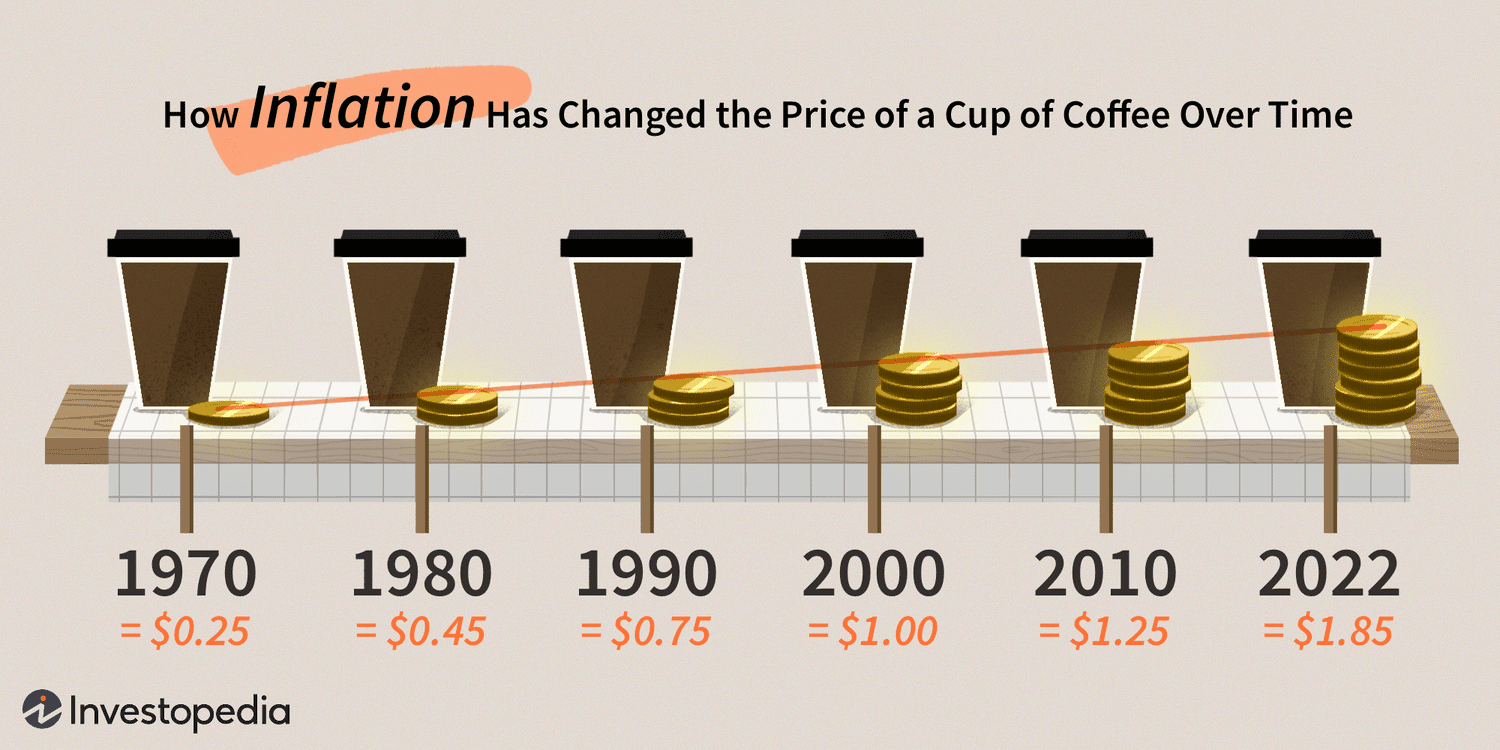
Inflation measures how much more expensive a set of goods and services has become over a certain period, usually a year. It may be one of the most familiar words in economics. Inflation has plunged countries into long periods of instability. Central bankers often aspire to be known as “inflation hawks.”
- demand-pull,
- cost-push, and.
- inflation expectations.
- Demand-pull inflation.
- Cost-push inflation.
- Built-in inflation.
Is inflation good or bad: While high inflation can be harmful, too little inflation can also weaken the economy. When the economy is struggling and inflation is too low, the Fed will take the opposite approach by lowering interest rates or buying assets to increase cash circulation.
In an inflationary environment, unevenly rising prices inevitably reduce the purchasing power of some consumers, and this erosion of real income is the single biggest cost of inflation. Inflation can also distort purchasing power over time for recipients and payers of fixed interest rates.
RECESSION

A recession begins when the economy reaches a peak of activity and ends when the economy reaches its trough.” Consistent with this definition, the Committee focuses on a comprehensive set of measures—including not only GDP, but also employment, income, sales, and industrial production—to analyze the trends in economic …
What Happens in a Recession? Economic output, employment, and consumer spending drop in a recession. Interest rates are also likely to decline as the central bank (such as the U.S. Federal Reserve Bank) cuts rates to support the economy






